Understanding Neural Networks: A Beginner's Guide
Neural networks are the backbone of modern artificial intelligence, powering everything from image recognition to natural language processing. But what exactly are they, and how do they work?
What is a Neural Network?
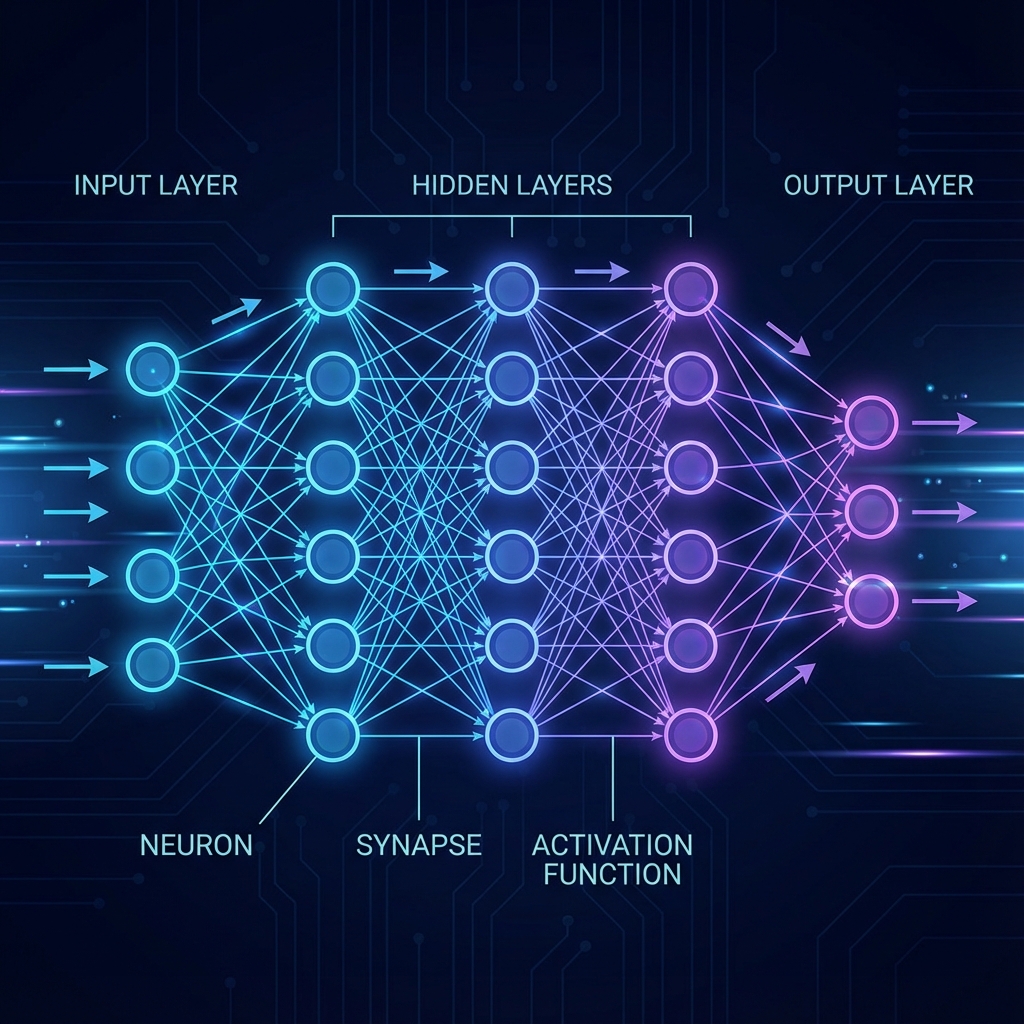
A neural network is a computational model inspired by the human brain. It consists of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized in layers that process information and learn patterns from data.
The Basic Structure
- Input Layer: Receives raw data
- Hidden Layers: Process and transform the data
- Output Layer: Produces the final result
How Neural Networks Learn
Neural networks learn through a process called backpropagation:
# Simplified neural network training
def train_network(network, data, labels, epochs):
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Forward pass
predictions = network.forward(data)
# Calculate loss
loss = calculate_loss(predictions, labels)
# Backward pass (backpropagation)
gradients = network.backward(loss)
# Update weights
network.update_weights(gradients)
Types of Neural Networks
1. Feedforward Neural Networks
The simplest type, where information flows in one direction from input to output.
2. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Specialized for processing grid-like data such as images.
3. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Designed for sequential data like text or time series.
4. Transformers
The architecture behind modern language models like GPT and BERT.
Real-World Applications
Neural networks are transforming industries:
- Healthcare: Disease diagnosis and drug discovery
- Finance: Fraud detection and algorithmic trading
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles
- Entertainment: Content recommendation systems
Getting Started with Neural Networks
If you're interested in building neural networks, here are some resources:
- Frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras
- Courses: Fast.ai, Coursera Deep Learning Specialization
- Practice: Kaggle competitions and personal projects
Conclusion
Neural networks represent a powerful tool for solving complex problems. While the mathematics can be intimidating, the core concepts are accessible to anyone willing to learn. Start small, experiment often, and gradually build your understanding.
Ready to dive deeper? Check out our advanced tutorials on specific neural network architectures.